Line Balancing - What is it ?
The Line Balancing Training module is part of our Lean Six Sigma Black Belt Certification course, which is now available with a 90% discount
Here is a simple definition and example of line balancing :
Everyone is doing the same amount of work
Doing the same amount of work to customer requirement
Variation is ‘smoothed’
No one overburdened
No one waiting
Everyone working together in a BALANCED fashion
Line Balancing Example
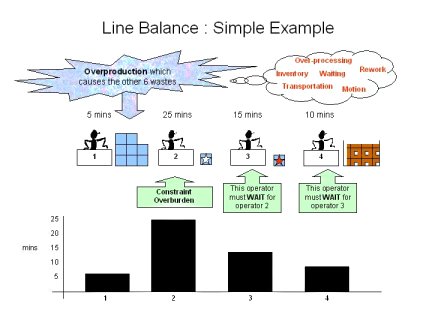
Here we see operator number 1 over-producing, thus creating the other 6 wastes.
We simply re-balance the work content (Re distribute some of the work), using a Yamazumi board as it is often known
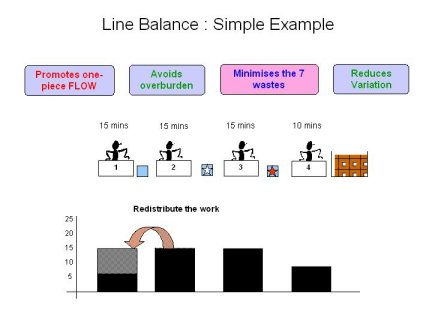
In the example shown above, the Line Balancing exercise looks incredibly simple - So why doesn't everyone do it ?
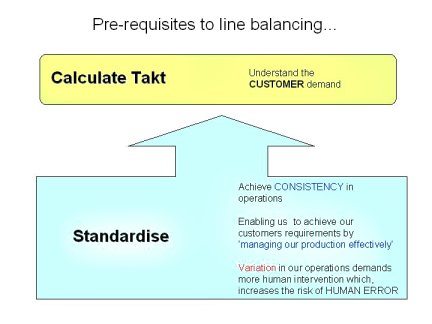
There are two vital pre requisites to balancing a line which must be in place before a yamazumi exercise can take place.
These are:
Takt Time & Standard Work
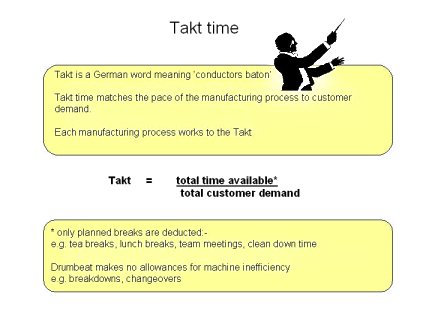
Takt Time for Line Balancing
Takt Time is the production "Drumbeat" based on customer demand
Standard Work for Line Balancing
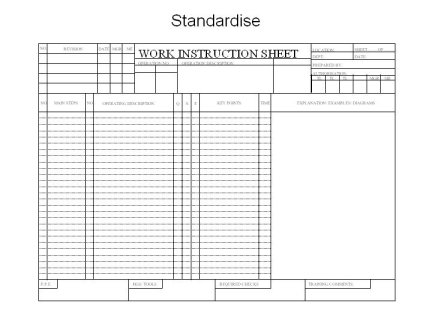
Whether you use Standard work combination tables, Standard work instruction sheets or any other Standard work documentation will depend upon the type of work involved
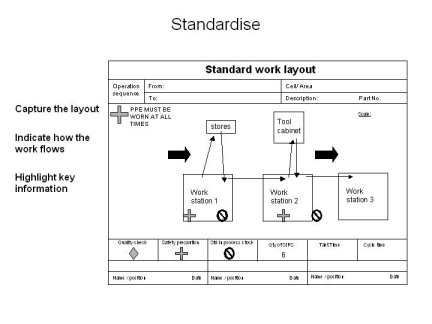
Standard Work instruction sheets provide a detailed description of HOW to do a particular step of a work operation. These provide a standard method of carrying out any particular task ensuring each task is repeatable and reproducible.
Benefits of the pre requisites:
Takt time maximises the productivity due to:
· Easily managed processes
. Workflow is matched to customer demand
· Output of each process matches customer demand
Standard Operations provide:
· Capable and repeatable processes
· Process control at source
· Improves accuracy of planning
· Better adherence to plans
· A platform from which continuous improvement can be made
· Reduced costs
· Improved quality
· Basis for training
Achieve CONSISTENCY in operations
Enabling us to achieve our customers requirements by ‘managing our production effectively’
Variation in our operations demands more human intervention which, increases the risk of HUMAN ERROR
Without standardisation, there can be NO improvement, according to Taichi Ohno. Contrary to common belief, every process can be standardised, the level of standardisation is only dependent upon the complexity of the process and the opportunity for external factors to introduce variability into the process (E.g. a telesales process would need to be at a higher level due to the variation that can be introduced by the customer, hence we would use a 'Framework', or 'Call structure' to ensure the process stays on track)
To advance your knowledge and career prospects using Lean Six Sigma, sign up for the black belt certification course which includes a module on Line Balancing